6. Graph optimization 파트 중요 코드 정리
1. Relocalization
1) int main(int argc, char **argv)
...
VISUALIZATION_SHIFT_X = 0;
VISUALIZATION_SHIFT_Y = 0;
SKIP_CNT = 0;
SKIP_DIS = 0;
cameraposevisual.setScale(0.1);
cameraposevisual.setLineWidth(0.01);
string vocabulary_file = pkg_path + "/../support_files/brief_k10L6.bin";
posegraph.loadVocabulary(vocabulary_file);
BRIEF_PATTERN_FILE = pkg_path + "/../support_files/brief_pattern.yml";
...
posegraph.setIMUFlag(USE_IMU);
ros::Subscriber sub_vio = n.subscribe("/vins_estimator/odometry", 2000, vio_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_image = n.subscribe(IMAGE_TOPIC, 2000, image_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_pose = n.subscribe("/vins_estimator/keyframe_pose", 2000, pose_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_extrinsic = n.subscribe("/vins_estimator/extrinsic", 2000, extrinsic_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_point = n.subscribe("/vins_estimator/keyframe_point", 2000, point_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_margin_point = n.subscribe("/vins_estimator/margin_cloud", 2000, margin_point_callback);
pub_match_img = n.advertise<sensor_msgs::Image>("match_image", 1000);
pub_camera_pose_visual = n.advertise<visualization_msgs::MarkerArray>("camera_pose_visual", 1000);
pub_point_cloud = n.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud>("point_cloud_loop_rect", 1000);
pub_margin_cloud = n.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud>("margin_cloud_loop_rect", 1000);
pub_odometry_rect = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("odometry_rect", 1000);
std::thread measurement_process;
std::thread keyboard_command_process;
measurement_process = std::thread(process);
keyboard_command_process = std::thread(command);
-
Three threads :
(1) measurement_process : process() :
(2) keyboard_command_process : command() : Just decide save or new start
(3) t_optimization : PoseGraph::optimze4DOF() -
Callbacks :
(1) Odometry (nav_msgs::Odometry, vio_callback) → rviz에서 camera visualize
(2) Image (sensor_msgs::Image, image_callback) → image_buf에 넣기 / 시간차이 너무 크면 loop closing하는 sequence 새로 시작.
(3) Keyframe Pose (nav_msgs::Odometry, pose_callback) →pose_buf에 넣기
(4) Extrinsic (nav_msgs::Odometry, extrinsic_callback) →tic, ric
(5) Keyframe Points (sensor_msgs::PointCloud, point_callback) → point_buf에 넣기, 계산된 dritft로 조정하여 points visualize
2) void process()
while (true)
{
sensor_msgs::ImageConstPtr image_msg = NULL;
sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr point_msg = NULL;
nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr pose_msg = NULL;
m_buf.lock();
if(!image_buf.empty() && !point_buf.empty() && !pose_buf.empty())
{
if (image_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() > pose_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec())
pose_buf.pop();
else if (image_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() > point_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec())
point_buf.pop();
else if (image_buf.back()->header.stamp.toSec() >= pose_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec()
&& point_buf.back()->header.stamp.toSec() >= pose_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec())
{
pose_msg = pose_buf.front();
pose_buf.pop();
while (!pose_buf.empty())
pose_buf.pop();
while (image_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() < pose_msg->header.stamp.toSec())
image_buf.pop();
image_msg = image_buf.front();
image_buf.pop();
while (point_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() < pose_msg->header.stamp.toSec())
point_buf.pop();
point_msg = point_buf.front();
point_buf.pop();
}
}
m_buf.unlock();
if (pose_msg != NULL)
{
if (skip_first_cnt < SKIP_FIRST_CNT)
{
skip_first_cnt++;
continue;
}
cv_bridge::CvImageConstPtr ptr;
if (image_msg->encoding == "8UC1")
{
sensor_msgs::Image img;
img.header = image_msg->header;
img.height = image_msg->height;
img.width = image_msg->width;
img.is_bigendian = image_msg->is_bigendian;
img.step = image_msg->step;
img.data = image_msg->data;
img.encoding = "mono8";
ptr = cv_bridge::toCvCopy(img, sensor_msgs::image_encodings::MONO8);
}
else
ptr = cv_bridge::toCvCopy(image_msg, sensor_msgs::image_encodings::MONO8);
cv::Mat image = ptr->image;
// build keyframe
Vector3d T = Vector3d(pose_msg->pose.pose.position.x,
pose_msg->pose.pose.position.y,
pose_msg->pose.pose.position.z);
Matrix3d R = Quaterniond(pose_msg->pose.pose.orientation.w,
pose_msg->pose.pose.orientation.x,
pose_msg->pose.pose.orientation.y,
pose_msg->pose.pose.orientation.z).toRotationMatrix();
if((T - last_t).norm() > SKIP_DIS)
{
vector<cv::Point3f> point_3d;
vector<cv::Point2f> point_2d_uv;
vector<cv::Point2f> point_2d_normal;
vector<double> point_id;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < point_msg->points.size(); i++)
{
cv::Point3f p_3d;
p_3d.x = point_msg->points[i].x;
p_3d.y = point_msg->points[i].y;
p_3d.z = point_msg->points[i].z;
point_3d.push_back(p_3d);
cv::Point2f p_2d_uv, p_2d_normal;
double p_id;
p_2d_normal.x = point_msg->channels[i].values[0];
p_2d_normal.y = point_msg->channels[i].values[1];
p_2d_uv.x = point_msg->channels[i].values[2];
p_2d_uv.y = point_msg->channels[i].values[3];
p_id = point_msg->channels[i].values[4];
point_2d_normal.push_back(p_2d_normal);
point_2d_uv.push_back(p_2d_uv);
point_id.push_back(p_id);
}
KeyFrame* keyframe = new KeyFrame(pose_msg->header.stamp.toSec(), frame_index, T, R, image,
point_3d, point_2d_uv, point_2d_normal, point_id, sequence);
m_process.lock();
start_flag = 1;
posegraph.addKeyFrame(keyframe, 1);
m_process.unlock();
frame_index++;
last_t = T;
}
}
std::chrono::milliseconds dura(5);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(dura);
}
- image (front) ≤ pose ≤ point(back) ≤ image(back) 순서가 되도록 맞추고, image_msg (front), pose_msg, point_msg를 각각 가져온다.
- pose_msg는 estimator에서의 Ps,Rs (third last), point_msg는 f_manager.feature에 해당한다.
-
(1) point_3d : 3D points of features
(2) point_2d_normal : noramlized된 image(third last frame) points
(3) point_2d_uv : image(third last frame)의 original points
(4) point_id : feature ids - KeyFrame 생성시 computeWindowBRIEFPoint(), computeBRIEFPoint() 가 실행된다.
3) void KeyFrame::computeWindowBRIEFPoint()
BriefExtractor extractor(BRIEF_PATTERN_FILE.c_str());
for(int i = 0; i < (int)point_2d_uv.size(); i++)
{
cv::KeyPoint key;
key.pt = point_2d_uv[i];
window_keypoints.push_back(key);
}
extractor(image, window_keypoints, window_brief_descriptors);
- Keyframe을 만들때, computeWindowBRIEFPoint(), computeBRIEFPoint() 함수를 호출하게 된다.
- uv(original image points)를 window_keypoints vector에 저장 후, BRIEF extractor를 통해 pattern file을 이용한 keypoints에 해당하는 descriptor (vector
) 를 만든다
4) void KeyFrame::computeBRIEFPoint()
BriefExtractor extractor(BRIEF_PATTERN_FILE.c_str());
const int fast_th = 20; // corner detector response threshold
if(1)
cv::FAST(image, keypoints, fast_th, true);
extractor(image, keypoints, brief_descriptors);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)keypoints.size(); i++)
{
Eigen::Vector3d tmp_p;
m_camera->liftProjective(Eigen::Vector2d(keypoints[i].pt.x, keypoints[i].pt.y), tmp_p);
cv::KeyPoint tmp_norm;
tmp_norm.pt = cv::Point2f(tmp_p.x()/tmp_p.z(), tmp_p.y()/tmp_p.z());
keypoints_norm.push_back(tmp_norm);
}
- FAST 알고리즘으로 corners가 detect되고, 이 점들을 undistortion과 normalize를 거쳐 keypoints_norm에 저장한다.
- brief_descriptor에는 불러온 것이 아닌 해당 이미지에서 FAST로 직접찾은 feature들의 description이 담겨 있다.
5) void PoseGraph::addKeyFrame(KeyFrame* cur_kf, bool flag_detect_loop)
Vector3d vio_P_cur;
Matrix3d vio_R_cur;
// Initialization : 처음에 sequence_cnt = 0, cur_kf->sequence = 1이라 실행됨.
if (sequence_cnt != cur_kf->sequence)
{
sequence_cnt++;
sequence_loop.push_back(0);
w_t_vio = Eigen::Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
w_r_vio = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
m_drift.lock();
t_drift = Eigen::Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
r_drift = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
m_drift.unlock();
}
cur_kf->getVioPose(vio_P_cur, vio_R_cur);
vio_P_cur = w_r_vio * vio_P_cur + w_t_vio;
vio_R_cur = w_r_vio * vio_R_cur;
cur_kf->updateVioPose(vio_P_cur, vio_R_cur);
cur_kf->index = global_index;
global_index++;
int loop_index = -1;
if (flag_detect_loop) // 항상 1, 0이면 db에 descriptor 추가하고 끝.
{
TicToc tmp_t;
loop_index = detectLoop(cur_kf, cur_kf->index);
}
if (loop_index != -1)
{
KeyFrame* old_kf = getKeyFrame(loop_index);
if (cur_kf->findConnection(old_kf))
{
if (earliest_loop_index > loop_index || earliest_loop_index == -1)
earliest_loop_index = loop_index;
Vector3d w_P_old, w_P_cur, vio_P_cur;
Matrix3d w_R_old, w_R_cur, vio_R_cur;
old_kf->getVioPose(w_P_old, w_R_old);
cur_kf->getVioPose(vio_P_cur, vio_R_cur);
Vector3d relative_t;
Quaterniond relative_q;
relative_t = cur_kf->getLoopRelativeT();
relative_q = (cur_kf->getLoopRelativeQ()).toRotationMatrix();
// 기존것 world기준에서 상대적인 t,R이용해서
// 지금 frame 위치를 world로 바꿈.
w_P_cur = w_R_old * relative_t + w_P_old;
w_R_cur = w_R_old * relative_q;
double shift_yaw;
Matrix3d shift_r;
Vector3d shift_t;
if(use_imu)
{
shift_yaw = Utility::R2ypr(w_R_cur).x() - Utility::R2ypr(vio_R_cur).x();
shift_r = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(shift_yaw, 0, 0));
}
else
shift_r = w_R_cur * vio_R_cur.transpose();
shift_t = w_P_cur - w_R_cur * vio_R_cur.transpose() * vio_P_cur;
// shift vio pose of whole sequence to the world frame
if (old_kf->sequence != cur_kf->sequence && sequence_loop[cur_kf->sequence] == 0)
{
w_r_vio = shift_r;
w_t_vio = shift_t;
vio_P_cur = w_r_vio * vio_P_cur + w_t_vio;
vio_R_cur = w_r_vio * vio_R_cur;
cur_kf->updateVioPose(vio_P_cur, vio_R_cur);
list<KeyFrame*>::iterator it = keyframelist.begin();
for (; it != keyframelist.end(); it++)
{
if((*it)->sequence == cur_kf->sequence)
{
Vector3d vio_P_cur;
Matrix3d vio_R_cur;
(*it)->getVioPose(vio_P_cur, vio_R_cur);
vio_P_cur = w_r_vio * vio_P_cur + w_t_vio;
vio_R_cur = w_r_vio * vio_R_cur;
(*it)->updateVioPose(vio_P_cur, vio_R_cur);
}
}
sequence_loop[cur_kf->sequence] = 1;
}
m_optimize_buf.lock();
optimize_buf.push(cur_kf->index);
m_optimize_buf.unlock();
}
}
...
keyframelist.push_back(cur_kf);
...
- initialize시에 vio_P_cur, vio_R_cur = $P_{b_k}^w$, $R_{b_k}^w$에 해당한다. 이 drift를 w_r_vio, w_t_vio로 고쳐주게 된다.
- getKeyFrame으로 loop detect된 frame index를 가져와서, findConnection 함수를 수행한다.
- old frame과 cur frame의 각각의 Pose를 얻어와, w_R_old로 world frame기준으로 바꾼후, w_P_cur, w_R_cur에 현재 frame의 world frame 기준 Pose를 저장한다. (relative_t, relative_q는 old frame과 cur frame의 feature matching 및 PnPRANSAC을 통해 상대적인 위치 차이를 구한 것이다.)
- translation과 yaw값의 shift를 구한다. (translation의 경우 IMU frame 기준으로 바꾼후, 다시 w_R_cur을 적용하하여 world frame으로 기준으로 바꾼 rotation값을 구한다.)
- old와 cur keyframe간의 sequence가 다른 경우에만, Relocalization을 통해 current keyframe의 위치를 update해준다. 또한 cur keyframe과 같은 sequence인 frame들의 위치도 전부 update해준다. sequence는 image_callback에 시간차가 큰 경우 달라진다.
- cur keyframe의 frame index를 optimize_buf에 추가하여 global optimization에 사용한다.
6) int PoseGraph::detectLoop(KeyFrame* keyframe, int frame_index)
QueryResults ret;
db.query(keyframe->brief_descriptors, ret, 4, frame_index - 50);
db.add(keyframe->brief_descriptors);
// ret[0] is the nearest neighbour's score. threshold change with neighour score
bool find_loop = false;
if (ret.size() >= 1 &&ret[0].Score > 0.05)
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < ret.size(); i++)
{
//if (ret[i].Score > ret[0].Score * 0.3)
if (ret[i].Score > 0.015)
{
find_loop = true;
}
}
if (find_loop && frame_index > 50)
{
int min_index = -1;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < ret.size(); i++)
{
if (min_index == -1 || (ret[i].Id < min_index && ret[i].Score > 0.015))
min_index = ret[i].Id;
}
return min_index;
}
else
return -1;
- DBoW2를 사용해 loop detection을 진행한다. ret에 결과가 저장되며, db.add를 통해 keyframe의 descriptor를 추가해준다. Default는 L1_NORM으로 설정되어 query를 비교한다.
- Score를 휴리스틱하게
(추정)정하여, loop 여부를 판단한다.
7) bool KeyFrame::findConnection(KeyFrame* old_kf)
matched_3d = point_3d;
matched_2d_cur = point_2d_uv;
matched_2d_cur_norm = point_2d_norm;
matched_id = point_id;
searchByBRIEFDes(matched_2d_old, matched_2d_old_norm, status, old_kf->brief_descriptors, old_kf->keypoints, old_kf->keypoints_norm);
reduceVector(matched_2d_cur, status);
reduceVector(matched_2d_old, status);
reduceVector(matched_2d_cur_norm, status);
reduceVector(matched_2d_old_norm, status);
reduceVector(matched_3d, status);
reduceVector(matched_id, status);
status.clear();
Eigen::Vector3d PnP_T_old;
Eigen::Matrix3d PnP_R_old;
Eigen::Vector3d relative_t;
Quaterniond relative_q;
double relative_yaw;
// Feature Retrieval
if ((int)matched_2d_cur.size() > MIN_LOOP_NUM)
{
PnPRANSAC(matched_2d_old_norm, matched_3d, status, PnP_T_old, PnP_R_old);
reduceVector(matched_2d_cur, status);
reduceVector(matched_2d_old, status);
reduceVector(matched_2d_cur_norm, status);
reduceVector(matched_2d_old_norm, status);
reduceVector(matched_3d, status);
reduceVector(matched_id, status);
}
if ((int)matched_2d_cur.size() > MIN_LOOP_NUM)
{
relative_t = PnP_R_old.transpose() * (origin_vio_T - PnP_T_old);
relative_q = PnP_R_old.transpose() * origin_vio_R;
relative_yaw = Utility::normalizeAngle(Utility::R2ypr(origin_vio_R).x() - Utility::R2ypr(PnP_R_old).x());
if (abs(relative_yaw) < 30.0 && relative_t.norm() < 20.0)
{
has_loop = true;
loop_index = old_kf->index;
loop_info << relative_t.x(), relative_t.y(), relative_t.z(),
relative_q.w(), relative_q.x(), relative_q.y(), relative_q.z(),
relative_yaw;
return true;
}
}
//printf("loop final use num %d %lf--------------- \n", (int)matched_2d_cur.size(), t_match.toc());
return false;
- searchByBRIEFDes함수에서, searchInAera(window_brief_descriptors[i], descriptors_old, keypoints_old, keypoints_old_norm, pt, pt_norm)를 호출하여 True일시 status.push_back(1) 아니면 0.
-
searchInAera함수 에서는, Hamming distance방식을 통해 descriptor의 거리를 비교한다. 이중 가장 근접한 feature의 point와 normalized point를 찾아 matched_2d_old, matched_2d_old_norm vector에 넣어주게 된다.
(이 점들이 Hamming Distance 80보다는 작아야하며, 그럴경우에만 True)
- 이 과정을 window_brief_descriptor, 즉 현재 frame의 feature에 대해 전부 진행한다. 즉, matched_2d_old에는 현재 frame와 loop detect된 old frame간에 매칭된 feature만 남게된다.
- reduceVector들로 해당 feature들만 남긴다.
- Outlier rejection을 위해 PnP RANSAC을 사용하여 correspondence를 찾고, (Feature Retrieval) reject 된 point는 삭제한다.
- 이전 값들과의 비교를 통해, 최종적으로 loop가 맞는지 판단한다. loop_info에는 상대적인 IMU frame 기준으로 상대적인 차이값이 저장(바뀌어야할 값)된다. 또한 loop_index에 loop closure해야하는 old keyframe의 index를 저장한다.
8) void KeyFrame::PnPRANSAC(const vectorcv::Point2f &matched_2d_old_norm, const std::vectorcv::Point3f &matched_3d, std::vector
cv::Mat r, rvec, t, D, tmp_r;
cv::Mat K = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0, 0, 0, 0, 1.0, 0, 0, 0, 1.0);
Matrix3d R_inital;
Vector3d P_inital;
Matrix3d R_w_c = origin_vio_R * qic;
// world frame 기준 body의 위치 + (body -> world) * (body frame 기준 camera의 위치)
Vector3d T_w_c = origin_vio_T + origin_vio_R * tic;
R_inital = R_w_c.inverse();
// world frame 기준 카메라의 위치 -> camera frame기준 world origin의 위치.
P_inital = -(R_inital * T_w_c);
cv::eigen2cv(R_inital, tmp_r);
cv::Rodrigues(tmp_r, rvec);
cv::eigen2cv(P_inital, t);
cv::Mat inliers;
if (CV_MAJOR_VERSION < 3)
solvePnPRansac(matched_3d, matched_2d_old_norm, K, D, rvec, t, true, 100, 10.0 / 460.0, 100, inliers);
else
{
if (CV_MINOR_VERSION < 2)
solvePnPRansac(matched_3d, matched_2d_old_norm, K, D, rvec, t, true, 100, sqrt(10.0 / 460.0), 0.99, inliers);
else
solvePnPRansac(matched_3d, matched_2d_old_norm, K, D, rvec, t, true, 100, 10.0 / 460.0, 0.99, inliers);
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int)matched_2d_old_norm.size(); i++)
status.push_back(0);
for( int i = 0; i < inliers.rows; i++)
{
int n = inliers.at<int>(i);
status[n] = 1;
}
cv::Rodrigues(rvec, r);
Matrix3d R_pnp, R_w_c_old;
cv::cv2eigen(r, R_pnp);
R_w_c_old = R_pnp.transpose();
Vector3d T_pnp, T_w_c_old;
cv::cv2eigen(t, T_pnp);
T_w_c_old = R_w_c_old * (-T_pnp);
PnP_R_old = R_w_c_old * qic.transpose();
PnP_T_old = T_w_c_old - PnP_R_old * tic;
-
origin_vio_R, origin_vio_T ($R_{b_k}^w$, $P_{b_k}^w$)를 통해, R_w_c, T_w_c ($R_{c_k}^w$, $P_{c_k}^w$) 를 구한다. 다음 수식을 참고하면
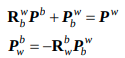
R_inital = rvec = $R^{c_k}_w$, P_initial = t = $P^{c_k}_w$이다.
- 논문에서는 Two step으로 2D - 2D → 3D - 2D 를 하는것으로 보이나, 코드상에서는 3D - 2D 한번만 수행한다. openCV의 solvePnPRansac함수를 통해, inliers points와 refined rvec, t를 얻는다. 이미 normalize되어 있어 K는 identity 함수, D는 empty matrix를 사용한다.
-
PnP_R_old, PnP_P_old ($R_{b_k}^w$, $P_{b_k}^w$) 를 최종적으로 구해 반환한다.
*
(R_w_c_old, T_w_c_old 이름 거꾸로 지은듯)
[reference] : https://docs.opencv.org/master/d9/d0c/group__calib3d.html#ga50620f0e26e02caa2e9adc07b5fbf24e
2. Pose Graph Optimization
[논문내용 발췌] Since our visual-inertial setup renders roll and pitch angles fully observable, the accumulated drift only occurs in four degrees-of-freedom
→ 4DOF에 대해서만 optimize가 필요하다.
1) void PoseGraph::optimize4DoF()
while(!optimize_buf.empty())
{
cur_index = optimize_buf.front();
first_looped_index = earliest_loop_index; // 가장 앞의 loop index
optimize_buf.pop();
}
if (cur_index != -1)
{
KeyFrame* cur_kf = getKeyFrame(cur_index);
int max_length = cur_index + 1;
// w^t_i w^q_i
double t_array[max_length][3];
Quaterniond q_array[max_length];
double euler_array[max_length][3];
double sequence_array[max_length];
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY;
options.max_num_iterations = 5;
ceres::LossFunction *loss_function;
loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(0.1);
ceres::LocalParameterization* angle_local_parameterization =
AngleLocalParameterization::Create();
list<KeyFrame*>::iterator it;
int i = 0;
for (it = keyframelist.begin(); it != keyframelist.end(); it++)
{
if ((*it)->index < first_looped_index)
continue;
(*it)->local_index = i;
Quaterniond tmp_q;
Matrix3d tmp_r;
Vector3d tmp_t;
(*it)->getVioPose(tmp_t, tmp_r);
tmp_q = tmp_r;
t_array[i][0] = tmp_t(0);
t_array[i][1] = tmp_t(1);
t_array[i][2] = tmp_t(2);
q_array[i] = tmp_q;
Vector3d euler_angle = Utility::R2ypr(tmp_q.toRotationMatrix());
euler_array[i][0] = euler_angle.x();
euler_array[i][1] = euler_angle.y();
euler_array[i][2] = euler_angle.z();
sequence_array[i] = (*it)->sequence; // frame 순서대로 sequence 저장.
problem.AddParameterBlock(euler_array[i], 1, angle_local_parameterization);
problem.AddParameterBlock(t_array[i], 3);
if ((*it)->index == first_looped_index || (*it)->sequence == 0)
{
problem.SetParameterBlockConstant(euler_array[i]);
problem.SetParameterBlockConstant(t_array[i]);
}
//add edge
for (int j = 1; j < 5; j++)
{
if (i - j >= 0 && sequence_array[i] == sequence_array[i-j])
{
Vector3d euler_conncected = Utility::R2ypr(q_array[i-j].toRotationMatrix());
Vector3d relative_t(t_array[i][0] - t_array[i-j][0], t_array[i][1] - t_array[i-j][1], t_array[i][2] - t_array[i-j][2]);
relative_t = q_array[i-j].inverse() * relative_t;
double relative_yaw = euler_array[i][0] - euler_array[i-j][0];
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = FourDOFError::Create( relative_t.x(), relative_t.y(), relative_t.z(),
relative_yaw, euler_conncected.y(), euler_conncected.z());
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, NULL, euler_array[i-j],
t_array[i-j],
euler_array[i],
t_array[i]);
}
}
//add loop edge
if((*it)->has_loop)
{
assert((*it)->loop_index >= first_looped_index);
int connected_index = getKeyFrame((*it)->loop_index)->local_index; // frame index
Vector3d euler_conncected = Utility::R2ypr(q_array[connected_index].toRotationMatrix());
Vector3d relative_t;
relative_t = (*it)->getLoopRelativeT();
double relative_yaw = (*it)->getLoopRelativeYaw();
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = FourDOFWeightError::Create( relative_t.x(), relative_t.y(), relative_t.z(),
relative_yaw, euler_conncected.y(), euler_conncected.z());
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, euler_array[connected_index],
t_array[connected_index],
euler_array[i],
t_array[i]);
}
if ((*it)->index == cur_index)
break;
i++;
}
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
i = 0;
for (it = keyframelist.begin(); it != keyframelist.end(); it++)
{
if ((*it)->index < first_looped_index)
continue;
Quaterniond tmp_q;
tmp_q = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(euler_array[i][0], euler_array[i][1], euler_array[i][2]));
Vector3d tmp_t = Vector3d(t_array[i][0], t_array[i][1], t_array[i][2]);
Matrix3d tmp_r = tmp_q.toRotationMatrix();
(*it)-> updatePose(tmp_t, tmp_r);
if ((*it)->index == cur_index)
break;
i++;
}
Vector3d cur_t, vio_t;
Matrix3d cur_r, vio_r;
cur_kf->getPose(cur_t, cur_r);
cur_kf->getVioPose(vio_t, vio_r);
m_drift.lock();
yaw_drift = Utility::R2ypr(cur_r).x() - Utility::R2ypr(vio_r).x();
r_drift = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(yaw_drift, 0, 0));
t_drift = cur_t - r_drift * vio_t;
m_drift.unlock();
it++;
for (; it != keyframelist.end(); it++)
{
Vector3d P;
Matrix3d R;
(*it)->getVioPose(P, R);
P = r_drift * P + t_drift;
R = r_drift * R;
(*it)->updatePose(P, R);
}
m_keyframelist.unlock();
updatePath();
}
- optimize_buf에는 loop closing 되야하는 cur keyframe의 frame index가 들어 있다.
- cur_index로 optimize_buf에 있는 가장 최근 frame index로 지정한다.
-
AngleLocalParameterization::Create()에서 ceres::AutoDiffLocalParameterization로 ceres::LocalParameterization에 대해 auto differentiation으로 jacobian을 구한다. AngleLocalParameterization 내부에서 operator()는 다음을 계산한다.
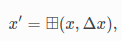
AddParameterBlock에서 size가 1인 이유는 yaw값만 추가해주기 때문이다.
만약 첫 loop index이거나 sequence가 0인 것들(load keyframe하는 경우)은 4DOF parameter들을 고정한다.
[reference] : http://ceres-solver.org/nnls_modeling.html#autodifflocalparameterization
-
Previous keyframe 4개에 대해 sequence가 같은 경우 edge로 추가한다.
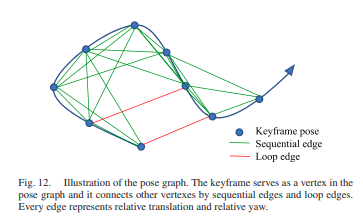
- loop가 detect된 frame에 대해 loop info를 활용하여 optimization에 추가 및 진행한다.
- 이후 update된 keyframe들의 Pose로 Keyframe들의 T_w_i, R_w_i 를 update해주고, 이후 추가적으로 들어온 frame들에 대해서의 Pose를 update해준다.
2) struct FourDOFError
FourDOFError(double t_x, double t_y, double t_z, double relative_yaw, double pitch_i, double roll_i)
:t_x(t_x), t_y(t_y), t_z(t_z), relative_yaw(relative_yaw), pitch_i(pitch_i), roll_i(roll_i){}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const yaw_i, const T* ti, const T* yaw_j, const T* tj, T* residuals) const
{
T t_w_ij[3];
t_w_ij[0] = tj[0] - ti[0];
t_w_ij[1] = tj[1] - ti[1];
t_w_ij[2] = tj[2] - ti[2];
// euler to rotation
T w_R_i[9];
YawPitchRollToRotationMatrix(yaw_i[0], T(pitch_i), T(roll_i), w_R_i);
// rotation transpose
T i_R_w[9];
RotationMatrixTranspose(w_R_i, i_R_w);
// rotation matrix rotate point
T t_i_ij[3];
RotationMatrixRotatePoint(i_R_w, t_w_ij, t_i_ij);
residuals[0] = (t_i_ij[0] - T(t_x));
residuals[1] = (t_i_ij[1] - T(t_y));
residuals[2] = (t_i_ij[2] - T(t_z));
residuals[3] = NormalizeAngle(yaw_j[0] - yaw_i[0] - T(relative_yaw));
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction* Create(const double t_x, const double t_y, const double t_z,
const double relative_yaw, const double pitch_i, const double roll_i)
{
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<
FourDOFError, 4, 1, 3, 1, 3>( // output(residual) dim / argument dims of operator()
new FourDOFError(t_x, t_y, t_z, relative_yaw, pitch_i, roll_i)));
}
double t_x, t_y, t_z;
double relative_yaw, pitch_i, roll_i;
- FourDOFError의 operator()에 parameter의 dimension은 1,3,1,3으로, yaw(prev kf), tranlsation(prev kf), yaw (cur kf),translation(cur kf)이다.
-
w_R_i에는 prev kf의 rotation이 들어간다. 이후 t_i_ij 값은 prev kf frame기준으로 prev kf와 cur kf와의 translation 차이를 갖게 된다. 이때 residual은 다음 식과 같이
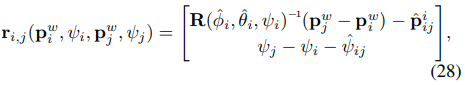
operator()에서 계산한 relative_t, relative yaw와 기존에 계산해준 값과의 차이가 된다.
처음에 둘이 같은 값을 가짐에도 residual이 되는 이유는, non-linear optimization이 iterative하게 진행됨에 따라 loop closing을 진행하면 기존에 계산해둔 relative_yaw는 인접 frame과의 차이를 상수를 갖고 있기 때문에 loop closing 후에 operator()에서 계산하는 relative 값이 바뀌게 되면 이에 맞춰서 인접 frame의 pose도 바꿔가면서 optimize하기 위함이다. (그래서 first_looped_index의 Pose는 상수로 고정하여 기준점으로 잡아주었다.)
물론 나중에 모든 keyframe의 Pose를 update하지만, optimize하는 Frame까지는 바꿔가며 optimize하게 된다.
AutoDiffCostFunction을 통해 jacobian은 자동 계산된다.
3) struct FourDOFWeightError
FourDOFWeightError(double t_x, double t_y, double t_z, double relative_yaw, double pitch_i, double roll_i)
:t_x(t_x), t_y(t_y), t_z(t_z), relative_yaw(relative_yaw), pitch_i(pitch_i), roll_i(roll_i){
weight = 1;
}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const yaw_i, const T* ti, const T* yaw_j, const T* tj, T* residuals) const
{
T t_w_ij[3];
t_w_ij[0] = tj[0] - ti[0];
t_w_ij[1] = tj[1] - ti[1];
t_w_ij[2] = tj[2] - ti[2];
// euler to rotation
T w_R_i[9];
YawPitchRollToRotationMatrix(yaw_i[0], T(pitch_i), T(roll_i), w_R_i);
// rotation transpose
T i_R_w[9];
RotationMatrixTranspose(w_R_i, i_R_w);
// rotation matrix rotate point
T t_i_ij[3];
RotationMatrixRotatePoint(i_R_w, t_w_ij, t_i_ij);
residuals[0] = (t_i_ij[0] - T(t_x)) * T(weight);
residuals[1] = (t_i_ij[1] - T(t_y)) * T(weight);
residuals[2] = (t_i_ij[2] - T(t_z)) * T(weight);
residuals[3] = NormalizeAngle((yaw_j[0] - yaw_i[0] - T(relative_yaw))) * T(weight) / T(10.0);
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction* Create(const double t_x, const double t_y, const double t_z,
const double relative_yaw, const double pitch_i, const double roll_i)
{
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<
FourDOFWeightError, 4, 1, 3, 1, 3>(
new FourDOFWeightError(t_x, t_y, t_z, relative_yaw, pitch_i, roll_i)));
}
double t_x, t_y, t_z;
double relative_yaw, pitch_i, roll_i;
double weight;
- 현재 갖고 있는 relative Pose와 PnP로 계산해둔 loop_info를 가지고 residual을 계산한다.
VINS-Fusion 코드를 정리한 포스트입니다.
- VINS-Fusion Code Review - (1) Image Processing
- VINS-Fusion Code Review - (2) IMU Processing
- VINS-Fusion Code Review - (3) Initialization
- VINS-Fusion Code Review - (4) Sliding window & Optimization
- VINS-Fusion Code Review - (5) Marginalization
- VINS-Fusion Code Review - (6) Graph optimization
Reference
- [2017] Quaternion kinematics for the error-state Kalman filter.pdf
- [2005] Indirect Kalman Filter for 3D Attitude Estimation.pdf
- Formula Derivation and Analysis of the VINS-Mono.pdf
- Marginalization&Shcurcomplement.pptx
- [TRO2012] Visual-Inertial-Aided Navigation for High-Dynamic Motion in Built Environments Without Initial Conditions.pdf
- VINS-Mono.pdf